These terms are excerpted from Alma’s in-depth guide on Israel and Palestine, which includes a lot of additional information. Read the entire guide here.
What are Israel and Palestine?
Israel: A state established in the Middle East in 1948 by the Israeli Declaration of Independence, which was immediately recognized by the United States and the Soviet Union.
Palestine: When people talk about Palestine today, they’re mainly referring to the Palestinian territories — the West Bank and Gaza Strip. But some also use “Palestine” to refer to the entire area between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, including pre-1967 Israel.
Read more about the history of the region here and here, and about the pre-state history here. Read about America’s role here.
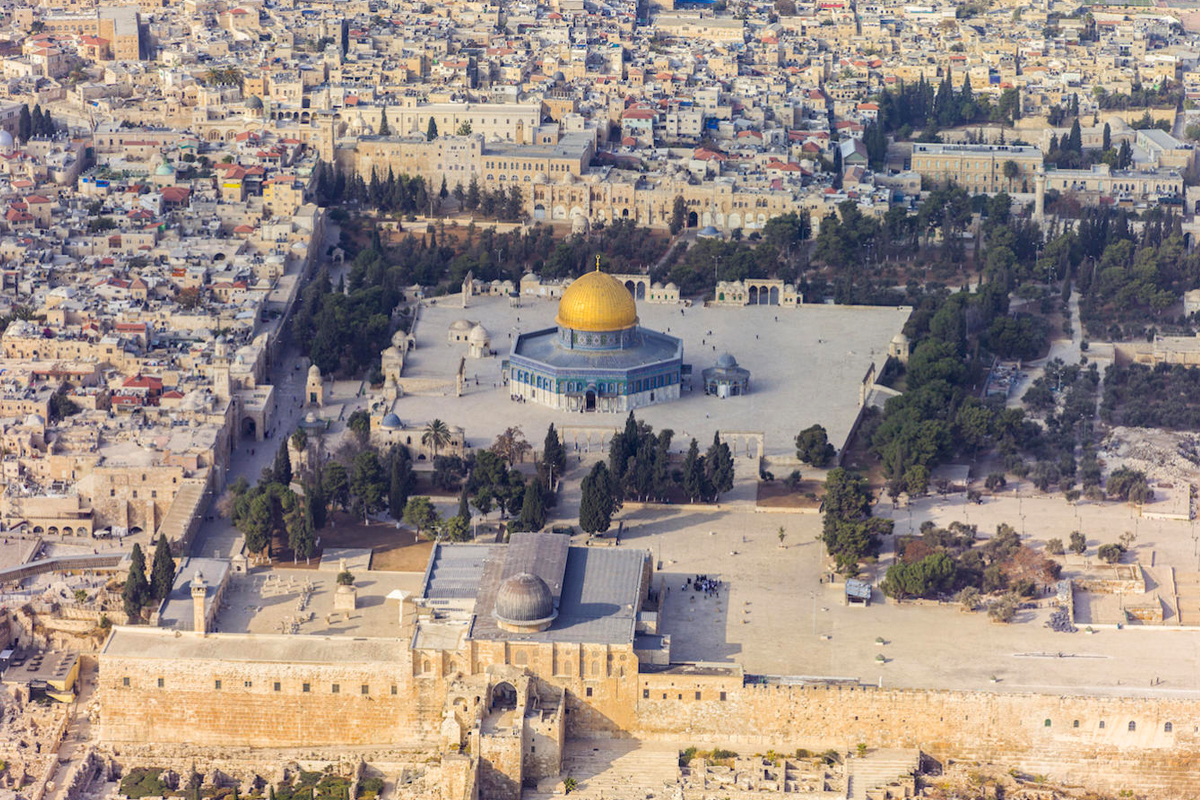
Jerusalem and its holy sites
What is Jerusalem? A city in the Middle East that is home to holy sites in Judaism, Islam and Christianity. It has two halves: a western portion that has been part of Israel since 1948 and is mostly home to Jews, and an eastern portion that Israel took over after the 1967 war that is mostly home to Palestinians. Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital.
What is the Temple Mount? The mount is the site from which Muslims believe Muhammad ascended to heaven and where the two Jewish temples once stood. It is the holiest site in Judaism, and the third holiest site in Islam.
What is Al-Aqsa Mosque? The Al-Aqsa Mosque is the name of the religious shrine that sits atop the Temple Mount in Jerusalem.
Read more about the recent conflicts at this holy site here and here.
What is the difference between the West Bank and Gaza?
Gaza is a coastal territory bordered by Israel, Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea. The strip was occupied by Israel following the 1967 war and returned to Palestinian control in 2005.The West Bank is the territory captured from Jordan by Israel in 1967. It remains the core piece of disputed territory between Israelis and Palestinians.
Read more about these territories here.
What is Zionism?
The definition of Zionism has evolved over time.
Pre-1948 Zionism was the general movement to establish a Jewish state. The modern state of Israel is therefore the culmination of Zionism, the Jewish effort to establish an autonomous state and end the diaspora of the Jewish people.
Post-1948 Zionism — arguably what most people consider the definition of Zionism today — can be simply defined as the belief that the State of Israel has a right to exist, that Jews have the right to self-determination. (This definition is up for debate, though.)
Read more about the history of Zionism here.
What is the Nakba?
Nakba means literally, in Arabic, “catastrophe.” Refers to 1948, when Palestinian Arabs fled or were expelled from their homes during the Independence War and the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
Right of Return: Palestinians call for a “right of return” that would permit them, and their descendants in perpetuity, to return to homes and villages they once fled or were forced to leave.
Law of Return: In 1950, Israel passed legislation stating “every Jew has the right to immigrate to the country,” creating a pathway for all Jews and spouses of Jews to immigrate to the country and obtain Israeli citizenship.
Learn more about intersectionality here.
What are Israeli settlements?
Settlements are Jewish communities established in territories captured by Israel during the Six-Day War, a war between Israel and multiple Arab states that took place over six days in June 1967.
Many consider these territories occupied by Israel, while Israel believes they are disputed territories over which there are competing claims.
Occupation, therefore, dates to 1967.
Settlements are located in three places: the West Bank, parts of Eastern Jerusalem, and the Golan Heights. There were settlements in Gaza, but they were evacuated in 2005, when 8,000 Jewish settlers were forcibly removed by the Israel Defense Forces.
Read more about settlements here.
What are the key Palestinian organizations to know?
The Palestinian Authority (PA) is a Palestinian governing body established for the purposes of Palestinian self-government by the 1994 Oslo Accords.
Hamas is an acronym for Harakat al-Muqawamah al-Islamiyya, or Islamic Resistance Movement. It is a militant Islamic organization that both engages in acts of terrorism against Israel and serves various social welfare functions. Founded as an offshoot of Egypt’s Muslim Brotherhood, Hamas became the governing authority in the Gaza Strip in 2007.
Read more about Palestinian politics here.
What is apartheid?
South Africa’s apartheid laws disenfranchised non-white South Africans and enforced a regime of comprehensive racial segregation.
A majority of the land in the West Bank is under Israeli military rule. Jewish settlers in the West Bank benefit from Israeli citizenship and can travel freely, sometimes on roads that were built just to serve them. By contrast, Palestinians can face long waits at Israeli army checkpoints to go from place to place.
Most Palestinians in the West Bank live under PA control, but for those living under Israeli military rule, Israel controls their access to natural resources and their ability to build homes. People and organizations, including Human Rights Watch, have accused Israel of apartheid in response to this situation — in which an Israeli military administration gives rights to Jewish settlers that West Bank Palestinians don’t have.
Read more about apartheid here.
What is the two-state solution?
Two states for two peoples, Israel and Palestine. Hypothetically, the Israel state would retain a Jewish majority, thus remaining a Jewish state, and the Palestinian state would have a Muslim Arab majority.
What is the one-state solution?
Also called the “binational state,” this would create one democratic, secular state in which both Israeli Jews and Palestinian Arabs would live as citizens with equal rights. Those who support a one-state solution generally see separating Israelis and Palestinians into two states as just too hard.
Are there other proposals that don’t fall under one-state vs. two-state? Yes. Read more here.